RESOURCES |+91 9204438764 |BOOK NOW

Psoriasis
Psoriasis
Psoriasis
Psoriasis
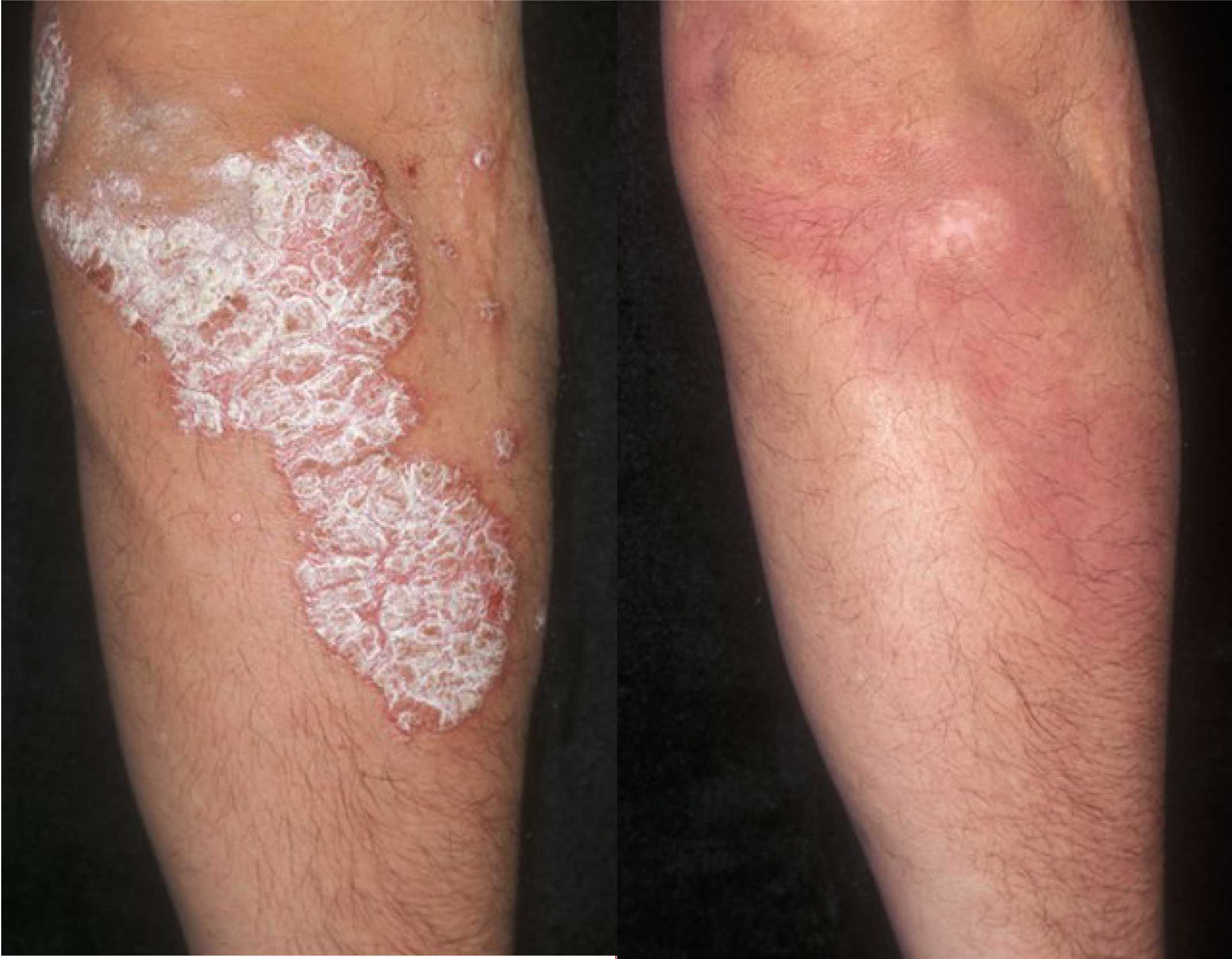
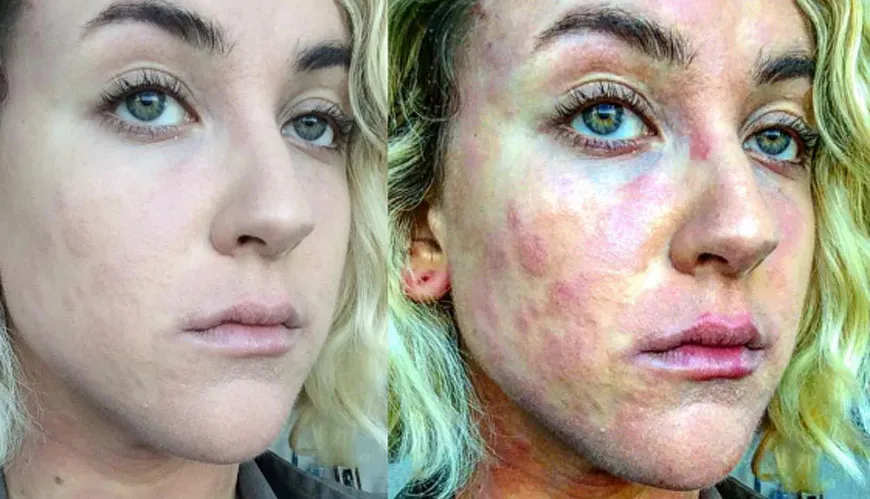
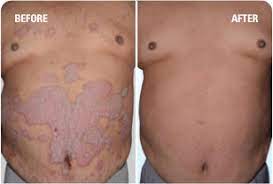
Psoriasis is a dry scaly skin disorder. Normally skin cells take about 28 days to replace themselves; however, this takes only 2-6 days in psoriasis patients. This rapid speeding up of skin cells replacement is caused by the mistakenly “switched on” immune system. The patient ends up with a rapid accumulation of skin cells that flakes .Psoriasis can sometimes affect the nails and joints. Very often, the nail plates are deformed with pitting, yellowish stain, thickened and disfigured nail plates.
Why do I get Psoriasis?
The cause of psoriasis is partly genetic and partly environmental. Very often, there is a positive family history in a patient with psoriasis. There is an increased risk of the children getting psoriasis if the parents or one of the parents has psoriasis. Environmental factors like physical or chemical injury to the skin, throat infection, reaction to certain drugs, hormonal changes, climate factors, mental and emotional stress can contribute to the onset and continuation of psoriasis.
Is it permanent? Can it be cured?
Psoriasis is an incurable disease. Most patients will have psoriasis for life and only a very small proportion of patients go into remission completely.
Is Psoriasis contagious?
Psoriasis is neither infectious or contagious. It cannot be passed on to other people.
Treatment options available
A special combination topical therapy is the current preferred treatment these days as it enables a quicker, more complete response with minimal or no local irritation to the skin. Separate scalp solution is often prescribed for treating psoriasis on the scalp.
Phototherapy is useful for the patient with more extensive rashes and for the patient who does not respond well to topical treatment. Phototherapy uses ultraviolet light to slow down the division of cells in the skin and is usually carried out 2 to 3 times a week. When the skin is clear of psoriasis, treatment is maintained and given less frequently.
Oral medications are usually reserved for patients with more severe disease and for patients who do not respond well to topical treatment and phototherapy. Drugs like Methotrexate, Cyclosporin A and Acitretin are very effective in the control of psoriasis; however, all these drugs have potential side effects. Blood tests need to be done regularly to monitor the drug effect on blood count, kidney and liver function.
This is a new class of drugs that come from psoriasis research. They are given as injections and they are very effective in controlling psoriasis. Their main advantage is the absence of organ damage to the kidney, liver and the ease and convenience of receiving the treatment. The main disadvantage is that the treatment is costly.